Diseases caused by numerous types of protozoa and helminths are widespread today. The danger of such ailments is explained not only by complications and malfunctions in the body, which lead to protozoa and worms in humans, but also by the complexity of diagnosing the disease due to the similarity of symptoms with various non-parasitic ailments.
Helminths and protozoa cause:
- malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract (constipation, diarrhea, vomiting);
- allergic skin reactions;
- general intoxication of the body;
- muscle and joint pain;
- dehydration.
In order to avoid a diagnostic error and the appointment of an inadequate course of treatment, which, at best, will simply be ineffective and, at worst, can cause complications, it is necessary to accurately determine the type of helminths and the degree of infection of the body with them.
Ways of infection with protozoan helminths
All worms enter the body from the outside. The same goes for the simplest helminths. In the environment, they live in the soil, in water bodies. In addition to unwashed hands, by eating poor quality products, you can be infected with them at home, through contact with a courier.
The main mechanism of any infection is most often fecal-oral, that is, a person simply swallows the eggs of the worm along with food, water, less often some helminth infestations occur when they are bitten by infected insects.
The simplest worms living in humans belong to the class of unicellular organisms. The infection is called protozoosis. Depending on the type and degree of invasion, the course of the disease can be severe, even leading to the death of the patient.
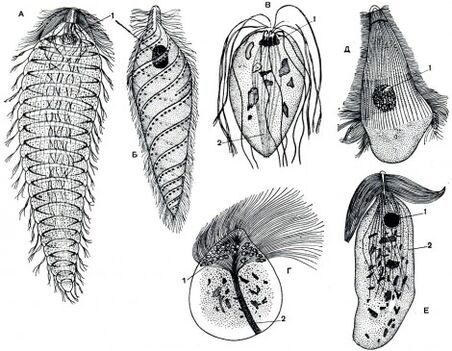
What helminths are called protozoa?
The simplest helminths can have a body of a constant shape (ciliates and flagellates) and a variable one, a bright representative of the amoeba. Their dimensions are very small and range from 4-5 micrometers to 1-3 millimeters. Often the cell of these microorganisms has several nuclei. The pseudopods, cilia and flagella act as organs of locomotion. The reproduction process, depending on the species, occurs by dividing in half or by a complex sexual method.
To protect themselves from adverse external conditions, as well as for further spread, simpler helminths can turn into cysts, which are cells covered with a protective membrane. This allows them to transform from an immobile cyst into an active state if they enter a favorable environment.
There are frequent situations when the courier's body does not notice even the simplest helminths parasitizing on it. In other cases, the invasion leads to the death of the host. For example, some species of antelope in Africa are permanent "masters" of trypanosomatids. And a human bite of the tsetse fly, which carries these helminths, can infect them and cause sleeping sickness, which is known to be life-threatening.
The most studied protozoan helminths
Parasites in the human body that belong to the class of flagellates:
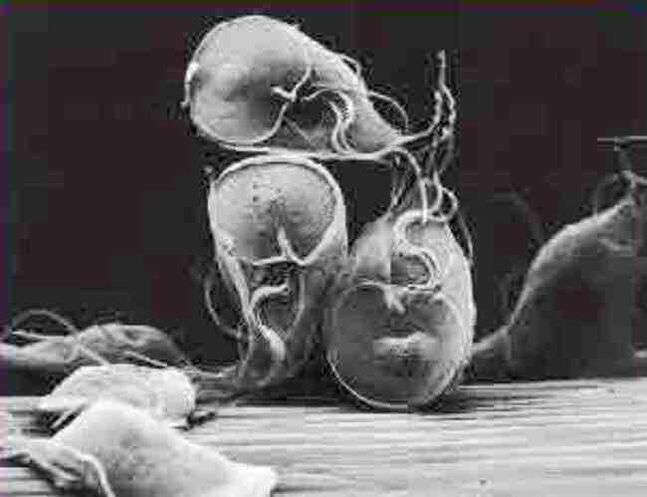
- Giardia is a parasite that usually lives in the intestines, bile ducts, liver of vertebrates (humans and animals). They can be transmitted through food, water, and other factors. This group of protozoa is the cause of a disease such as giardiasis, a functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, or the small intestine. Many patients infected with Giardia have no obvious symptoms.
- Leishmania are the simplest helminths carried by mosquitoes. After being bitten by insects, a person is more likely to have leishmaniasis. The signs of the disease are damage to the skin, mucous membranes and some internal organs, often fever and anemia become signs of the disease.
- Trypanosomatids are protozoa transmitted by insects. When infected, they cause trypanosomiasis disease. This disease has a long course. Depending on the type of trypanosomatids, various systems and organs are affected.
- Dysentery of the parasitic amoeba the intestine. The invasion is carried out in the form of a 4-nucleus cyst. Although the dysenteric amoeba is found almost everywhere, the most frequent cases of infection are recorded in tropical countries. Amoeba is the cause of such an infectious protozoan disease in humans as amoebiasis. The clinical picture of the disease is ulcerative colitis, characterized by relapses and exacerbations. There are also cases of an extra-intestinal form of amoebiasis - these protozoan helminths pass from the intestines to other organs and even to the skin. The last form of the disease is called skin amoebiasis: on the buttocks and in the perineum there are obvious ulcerative necrotic signs.
- Trichomonas causes trichomoniasis. Several subspecies of Trichomonas are currently being studied. Intestinal, the area of parasitism of which is located in the large intestine, and the helminth does not cause much damage to the intestine. The area of parasitism of the genitourinary Trichomonas, as can be seen from the name - the genitourinary system. The infection is carried out sexually. This subspecies of protozoa is the cause of a disease such as trichomoniasis. This infectious disease is manifested by inflammation of the genitourinary system. Oral Trichomonas parasite in the oral cavity, does not represent a danger to humans.
The sporophytic species of protozoa is represented by plasmodium and malarial coccidia:
- Malarial Plasmodium, transmitted by mosquitoes and a cause of malaria, is the simplest microorganism. Parasite in the blood. Malaria in someone infected with this parasite manifests itself with the following symptoms: hypochromic anemia, attacks of fever, enlargement of organs such as the liver and spleen.
- Coccidia are protozoa that live in the intestinal epithelial tissue of many animals. A number of coccidia species are the causative agents of a disease such as coccidiosis. In humans, this disease occurs with slight intoxication and the phenomena of gastroenteritis or enteritis.
Ciliates: balantides. This detachment of protozoa living in the large intestine is the cause of a disease such as infuser dysentery (balantidiasis).
Diagnosis and treatment of helminth protozoa
Most often, when the presence of helminths in the body occurs without symptoms, the disease is not diagnosed for a long time. Invasion can be suspected by specific symptoms and can only be detected with the help of laboratory tests on feces, urine, blood, fluids obtained by puncture from various organs and systems.
In medical practice, there are general principles for the treatment of protozoal invasion:
- antiparasitic drugs;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- detoxification medications;
- with the manifestation of a secondary bacterial infection, closely targeted antibiotics.
A specific treatment is prescribed by a doctor, based on the type of protozoan helminth and the degree of invasion.




































